Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?
BD Pharmingen™ Fluo-4 AM
(RUO)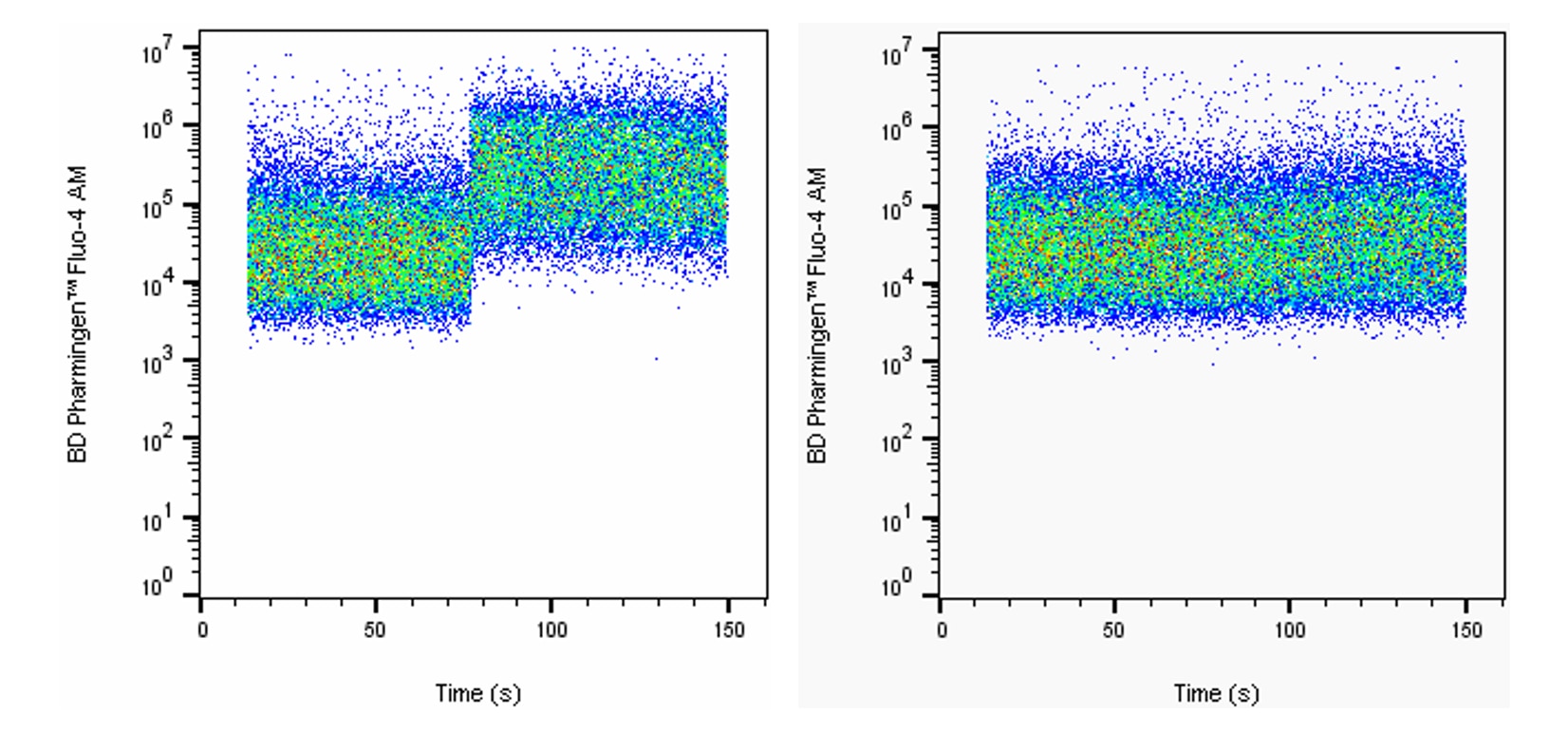


Intracellular calcium response of Jurkat cells to stimulation with A23187. Jurkat cells were stained with 5 μM BD Pharmingen™ Fluo-4 AM (Cat. No. 565878) in DPBS with calcium and magnesium for 20 minutes at 37°C. Cells were pelleted once and further incubated in complete medium for 30 minutes to allow complete hydrolysis of AM moieties. Cells were then pelleted and resuspended in DPBS with calcium and magnesium and analyzed on an BD Accuri™ C6 in the FL-1 channel. After 30 seconds of acquisition, 1 μM calcium ionophore A23187 (left, Sigma Aldrich Cat. No. C7522) or DMSO vehicle (right) was added to the tube, followed by mixing with the pipette. Jurkat cells show an increase in intracellular calcium concentration with addition of calcium ionophore A23187, but not with addition of DMSO vehicle.

BD Pharmingen™ Fluo-4 AM
Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Recommended Assay Procedures
Preparation
Bring Fluo-4 AM dye powder and anhydrous Dimethyl Sulfoxide to room temperature. Add 9 μl of DMSO to dye powder and vortex solution well. Inspect the solution and repeat vortex until the stock dye has fully dissolved. This yields a 5 mM stock solution.
Storage
Upon arrival, store the dry dye desiccated and protected from light at -20°C until use. We recommend a fresh vial of dye be used for each experiment and that reconstituted dye be discarded after use. However, if stock solutions are to be kept for use, they should be stored desiccated and protected from light at -20°C and used within one week of reconstitution.
Cytometry Requirements
Blue (eg, 488 nm) laser-equipped flow cytometers (eg, BD Accuri™ C6, BD LSRFortessa™, BD LSRFortessa™ X-20, or BD™ LSR II) can be used. This dye can be read out of filters commonly used for FITC or Alexa Fluor® 488 (eg, 530/30).
Fluorescence compensation is best achieved using a sample of the cells of interest stained with the dye. When designing multicolor panels, please be aware of spillover into the PE and BD Horizon™ PE-CF594 channels on the blue laser. If available, collecting these fluorochromes using the yellow-green (eg, 561 nm) laser may be advantageous to avoid spillover from Fluo-4 AM. Panels should be optimized to take this spillover into account.
Procedure
BD Pharmingen™ Fluo-4 AM Labeling of Cells
1. Prepare a single cell suspension at 1×10e6 cells/mL in physiologic loading buffer of choice.
• If serum is used in the loading buffer, it should be heat inactivated in order to prevent residual serum esterase activity from cleaving AM moieties on the dye prior to entry into cells.
2. Add dye stock solution for a final staining concentration of 1 - 5 μM and vortex immediately.
• We recommend using the lowest dye concentration that still yields sufficient signal in order to avoid dye toxicity, compartmentalization, and calcium buffering.
3. Incubate 15 - 60 minutes at 37°C.
• It is reported that dye compartmentalization is less significant at lower loading temperatures. In this case, it may be advantageous to load cells at room temperature if dye compartmentalization is significant for the cell type of interest.
4. Wash once and resuspend in analysis buffer of choice.
• For some cell types, it may be advantageous to incubate cells for another 30 minutes to allow complete de-esterification of AM moieties. In this case, cells should be incubated in physiologic buffer of choice or complete medium, washed once more, and then resuspended in analysis buffer of choice.
5. Proceed to flow cytometry.
Product Notices
- Alexa Fluor® is a registered trademark of Molecular Probes, Inc., Eugene, OR.
- Before staining with this reagent, please confirm that your flow cytometer is capable of exciting the fluorochrome and discriminating the resulting fluorescence.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
BD Pharmingen™ Fluo-4 AM is a cell-permeant dye that can be used to measure the intracellular ionized calcium concentration, [Ca2+]i. The hydrophobic acetomethoxy (AM) moiety allows passage across the cell membrane into viable cells. Once inside, intracellular esterases cleave the AM groups, leaving Fluo-4 trapped with the cell and free to bind intracellular calcium. The Kd for Ca2+ is approximately 335 nM in physiologic buffers.
Calcium-bound BD Pharmingen™ Fluo-4 AM has an excitation maximum of 494 nm and an emission maximum of 506 nm.
Development References (7)
-
Assinger A, Volf I, Schmid D. A novel, rapid method to quantify intraplatelet calcium dynamics by ratiometric flow cytometry.. PLoS ONE. 2015; 10(4):e0122527. (Methodology). View Reference
-
Bruton JD, Cheng AJ, Westerblad H. Methods to detect Ca(2+) in living cells.. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012; 740:27-43. (Methodology). View Reference
-
June CH, Abe R, Rabinovitch PS. Measurement of intracellular calcium ions by flow cytometry.. Curr Protoc Cytom. 2001; Chapter 9:Unit 9.8. (Methodology). View Reference
-
June CH, Moore JS. Measurement of intracellular ions by flow cytometry.. Curr Protoc Immunol. 2004; Chapter 5:Unit 5.5. (Methodology). View Reference
-
Ledderose C, Bao Y, Ledderose S, et al. Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Depleted Purinergic Signaling, and Defective T Cell Vigilance and Immune Defense.. J Infect Dis. 2016; 213(3):456-64. (Methodology). View Reference
-
Orbán C, Bajnok A, Vásárhelyi B, Tulassay T, Toldi G. Different calcium influx characteristics upon Kv1.3 and IKCa1 potassium channel inhibition in T helper subsets.. Cytometry A. 2014; 85(7):636-41. (Methodology). View Reference
-
Wiedemann A, Depoil D, Faroudi M, Valitutti S. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes kill multiple targets simultaneously via spatiotemporal uncoupling of lytic and stimulatory synapses.. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006; 103(29):10985-90. (Methodology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.