Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


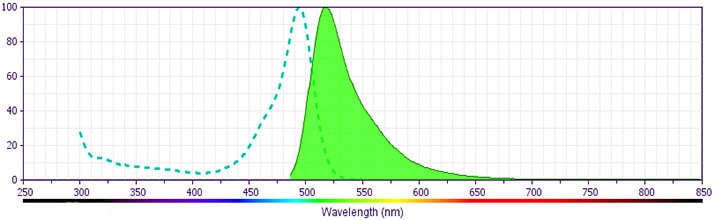
FITC Mouse Anti-Human CD23
Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
The CD23 antibody, clone EBVCS-5, is derived from the hybridization of Sp2/0 mouse myeloma cells with spleen cells from BALB/c mice immunized with an in vitro–transformed EBV cell line. The CD23 antibody recognizes a 45-kilodalton (kDa) type II membrane glycoprotein, which is a human B-lymphocyte differentiation antigen. The CD23 antigen is also known as the low affinity IgE receptor, Fc epsilon RII, and FcεRII.
Development References (14)
-
Capron M, Jouault T, Prin L, et al. Functional study of a monoclonal antibody to IgE Fc receptor (Fc epsilon R2) of eosinophils, platelets, and macrophages.. J Exp Med. 1986; 164(1):72-89. (Biology). View Reference
-
Centers for Disease Control. Update: universal precautions for prevention of transmission of human immunodeficiency virus, hepatitis B virus, and other bloodborne pathogens in healthcare settings. MMWR. 1988; 37:377-388. (Biology).
-
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2005. (Biology).
-
Gordon J, Rowe M, Walker L, Guy G. Ligation of the CD23,p45 (Blast-2, EBVCS) antigen triggers the cell-cycle progression of activated B lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1986; 16:1075-1080. (Biology).
-
Gordon J, Webb AJ, Walker L, Guy GR, Rowe M. Evidence of an association between CD23 and the receptor for a low molecular weight B cell growth factor. Eur J Immunol. 1986; 16:1627-1630. (Biology).
-
Kikutani H, Inui S, Sato R, et al. Molecular structure of human lymphocyte receptor for immunoglobulin E.. Cell. 1986; 47(5):657-65. (Biology). View Reference
-
Kikutani H, Suemura M, Owaki H, et al. Fc epsilon receptor, a specific differentiation marker transiently expressed on mature B cells before isotype switching.. J Exp Med. 1986; 164(5):1455-69. (Biology). View Reference
-
Kintner C, Sugden B. Identification of antigenic determinants unique to the surfaces of cells transformed by Epstein-Barr Virus. Nature. 1981; 294:458-460. (Biology).
-
Kwon HS, Park MC, Kim DG, et al. Identification of CD23 as a functional receptor for the proinflammatory cytokine AIMP1/p43. J Cell Sci. 2012; 125:4620-4629. (Biology).
-
Nadler LM. Reinherz EL, Haynes BF, Nadler LM, Bernstein ID, ed. Leukocyte Typing II: Human B Lymphocytes. New York, NY: Springer-Verlag; 1986:25-26.
-
Sherr E, Macy E, Kimata H, Gilly M, Saxon A. Binding the low affinity Fc ε R on B cells suppresses ongoing human IgE synthesis. J Immunol. 1989; 142:481-489. (Biology).
-
Thorley-Lawson D, Nadler L, Bhan A, Schooley R. Blast-2 (EBVCS), an early cell surface marker of human B cell activation, is superinduced by Epstein Barr Virus. J Immunol. 1985; 134:3007-3012. (Biology).
-
Yukawa K, Kikutani H, Owaki H, et al. A B-cell– specific differentiation antigen, CD23, is a receptor for IgE (FcεR) on lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1987; 138:2576-2580. (Biology).
-
van Dongen JJ, Lhermitte L, Böttcher S, et al. EuroFlow antibody panels for standardized n-dimensional flow cytometric immunophenotyping of normal, reactive and malignant leukocytes. Leukemia. 2012; 26(9):1908-1975. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Although not required, these products are manufactured in accordance with Good Manufacturing Practices.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.