Old Browser
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?
.png)
.png)
Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
BD™ CompBeads can be used as surrogates to assess fluorescence spillover (Compensation). When fluorochrome conjugated antibodies are bound to BD CompBeads, they have spectral properties very similar to cells. However, for some fluorochromes there can be small differences in spectral emissions compared to cells, resulting in spillover values that differ when compared to biological controls. It is strongly recommended that when using a reagent for the first time, users compare the spillover on cells and BD CompBead to ensure that BD CompBeads are appropriate for your specific cellular application.
Product Notices
- Researchers should determine the optimal concentration of this reagent for their individual applications.
- The production process underwent stringent testing and validation to assure that it generates a high-quality conjugate with consistent performance and specific binding activity. However, verification testing has not been performed on all conjugate lots.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Alexa Fluor™ is a trademark of Life Technologies Corporation.
- Please refer to http://regdocs.bd.com to access safety data sheets (SDS).
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- This product is provided under an Agreement between BIOTIUM and BD Biosciences. This product, and only in the amount purchased by buyer, may be used solely for buyer’s own internal research, in a manner consistent with the accompanying product literature. No other right to use, sell or otherwise transfer (a) this product, or (b) its components is hereby granted expressly, by implication or by estoppel. This product is for research use only. Diagnostic uses require a separate license from Biotium, Inc. For information on purchasing a license to this product including for purposes other than research, contact Biotium, Inc., 3159 Corporate Place, Hayward, CA 94545, Tel: (510) 265-1027. Fax: (510) 265-1352. Email: btinfo@biotium.com.
Companion Products




.png?imwidth=320)
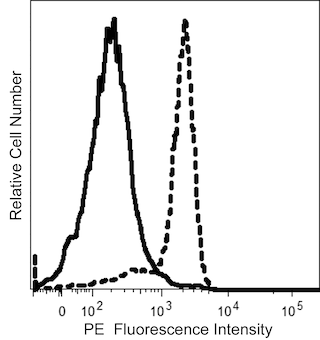
The CG4.rMab is a recombinant monoclonal antibody that was derived from CG4 hybridoma cells. The CG4.rMab specifically binds to human G-protein coupled receptor 56 (GPR56) like the conventional CG4 antibody and performs like the CG4 antibody when used to stain cells and analyze them by flow cytometry. GPR56 is also known as adhesion G-protein coupled receptor G1 (ADGRG1), or TM7XN1. GPR56 is a ~15kDa G protein-coupled receptor encoded by ADGRG1 which belongs to the adhesion-GPCR family that comprises 33 members in human. The extracellular region contains a mucin-like domain followed by a membrane proximal GPCR-autoproteolysis inducing (GAIN) domain, seven transmembrane regions and a cytoplasmic tail. The constitutive self-cleavage at the proteolytic site gives rise to a membrane spanning (C-terminal fragment or CTF) and an extracellular (N-terminal fragment or NTF) subunit that remain noncovalently bound, leading to the expression of a heterodimeric receptor at the cell surface. GPR56 is widely expressed with the highest levels of messenger found in the brain, heart, and thyroid gland. Recently, GPR56 was found to be variably expressed on platelets, cytotoxic NK cells and T lymphocytes including CD4+, CD8+, and γδ T cells. It was shown that GPR56 functions as an inhibitory receptor on NK cells through interaction with CD81. While GPR56 NTF associates with Tissue transglutaminase 2 and Collagen III (α-1), GPR56 CTF can recruit Gα proteins leading to the activation of mTOR and RhoA signaling pathways. GPR56 has been implicated in cell-cell interactions, adhesion, migration, and regulation of cell proliferation and survival of various cell types. New evidence also shows a role of GPR56 in tumor progression. Recently, the CG4 antibody was found to activate GPR56 in melanoma cells leading to an increase of IL-6 secretion, in a CD9/CD81-dependent manner.
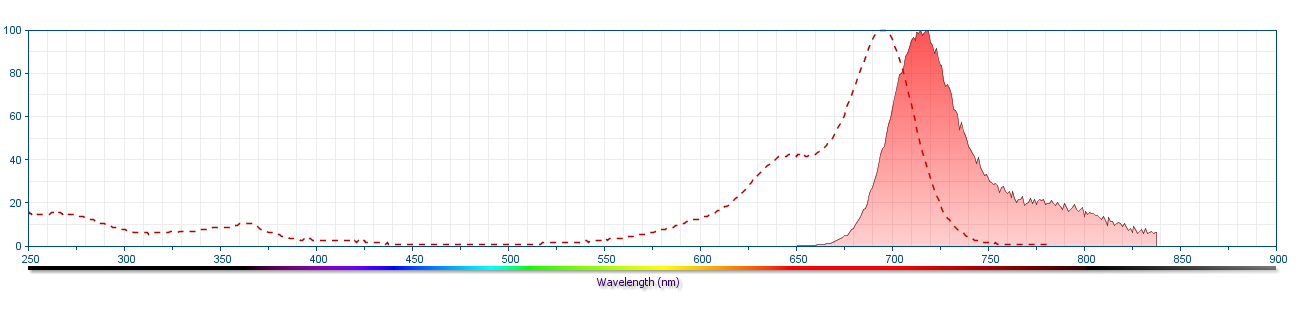
The antibody was conjugated to BD Horizon Red 718, which has been developed exclusively for BD Biosciences as a better alternative to Alexa Fluor™ 700. BD Horizon Red 718 can be excited by the red laser (628 – 640 nm) and, with an Em Max around 718 nm, it can be detected using a 730/45 nm filter. Due to similar excitation and emission properties, we do not recommend using R718 in combination with APC-R700 or Alexa Fluor™ 700.
Development References (6)
-
Della Chiesa M, Falco M, Parolini S, et al. GPR56 as a novel marker identifying the CD56dull CD16+ NK cell subset both in blood stream and in inflamed peripheral tissues.. Int Immunol. 2010; 22(2):91-100. (Biology: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Liu M, Parker RM, Darby K, et al. GPR56, a novel secretin-like human G-protein-coupled receptor gene.. Genomics. 1999; 55(3):296-305. (Biology). View Reference
-
Pabst C, Bergeron A, Lavallée VP, et al. GPR56 identifies primary human acute myeloid leukemia cells with high repopulating potential in vivo.. Blood. 2016; 127(16):2018-27. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Peng YM, van de Garde MD, Cheng KF, et al. Specific expression of GPR56 by human cytotoxic lymphocytes.. J Leukoc Biol. 2011; 90(4):735-40. (Immunogen: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Piao X, Hill RS, Bodell A, et al. G protein-coupled receptor-dependent development of human frontal cortex.. Science. 2004; 303(5666):2033-6. (Biology). View Reference
-
Rao TN, Marks-Bluth J, Sullivan J, et al. High-level Gpr56 expression is dispensable for the maintenance and function of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells in mice.. Stem Cell Res. 2015; 14(3):307-22. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical Data Sheets before using this product as described.
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.