Old Browser
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?






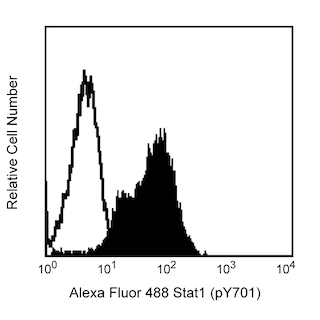
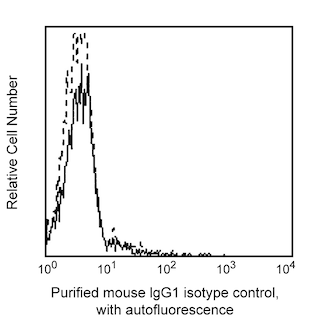
Analysis of PTF1A expression in rat pancreatic acinar cells by western blot and flow cytometry. Left panel: Lysates of the AR42J cell line (ATCC CRL-1492) were electrophoresed (SDS-PAGE) in a 4-20% Tris-Glycine polyacrylamide gel, transferred to PVDF membranes and then probed with 2 (lane 1), 1 (lane 2), 0.5 (lane 3), 0.25 (lane 4) mg/mL of Purified Mouse anti-PTF1A. Specific staining was detected with HRP Goat Anti-Mouse Ig (Cat. No. 554002). Right panel: AR42J cells were fixed in BD Cytofix™ Fixation Buffer (Cat. No. 554655), permeabilized with BD Phosflow™ Perm Buffer III (Cat. No. 558050) and stained with matching concentrations of either Purified Mouse IgG1, κ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 554121; dashed line) or Purified Mouse anti-PTF1A monoclonal antibody (solid line). The second-step reagent was PE Goat Anti-Mouse Ig (550589). The fluorescence histograms were derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of intact AR42J cells. Flow cytometry was performed using a BD LSRFortessa™ Flow Cytometer System.

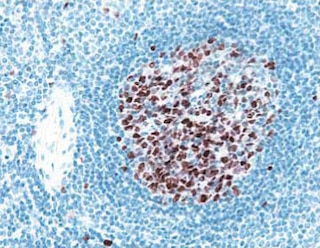
Immunohistochemical analysis of PTF1A expression by acinar cells within the human pancreas. Following antigen retrieval with BD Retrievagen A Buffer (Cat. No. 550524), the formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections were stained with either Purified Mouse IgG1 κ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 550878; left panel) or Purified Mouse anti-PTF1A antibody (right panel). A three-step staining procedure that employs Biotin Goat Anti-Mouse Ig (Cat. No. 550337), Streptavidin- HRP (Cat. No. 550946), and the DAB Substrate Kit (Cat. No. 550880) was used to develop the primary staining reagents. The acinar cell nuclei and cytoplasm stained positively for the expression of PTF1A. Original magnification: 40×.


BD Pharmingen™ Purified Mouse Anti-PTF1A

BD Pharmingen™ Purified Mouse Anti-PTF1A

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Sodium azide is a reversible inhibitor of oxidative metabolism; therefore, antibody preparations containing this preservative agent must not be used in cell cultures nor injected into animals. Sodium azide may be removed by washing stained cells or plate-bound antibody or dialyzing soluble antibody in sodium azide-free buffer. Since endotoxin may also affect the results of functional studies, we recommend the NA/LE (No Azide/Low Endotoxin) antibody format, if available, for in vitro and in vivo use.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Species cross-reactivity detected in product development may not have been confirmed on every format and/or application.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
Companion Products



The S25-763 monoclonal antibody specifically binds PTF1A (Pancreas specific transcription factor 1a). PTF1A is a transcription factor that contains a basic helix-loop-helix motif domain and, in combination with p75 and p64, forms the pancreas transcription factor complex. PTF1A plays a roles in pancreatic and cerebellar development. In early pancreatic development, pancreatic bud cells can either continue to pancreatic organogenesis or regress to a duodenal fate, and PTF1A plays a role in this differentiation. In late pancreatic development, the expression of PTF1A is restricted to acinar cells where it is involved in the maintenance of exocrine-specific gene expression. PTF1A expression is often evaluated to monitor pancreatic lineage differentiation from pluripotent stem cells. In addition, PTF1A is expressed during retinal development, and mutations in PTF1A cause cerebellar deficiencies.
This mouse anti-human PTF1A monoclonal antibody, clone S25-763, has been demonstrated to cross-react with rat and mouse pancreatic acinar cells.
Development References (7)
-
Kelly OG, Chan MY, Martinson LA, et al. Cell-surface markers for the isolation of pancreatic cell types derived from human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2011; 29(8):750-756. (Biology). View Reference
-
Krapp A, Knöfler M, Ledermann B, et al. The bHLH protein PTF1-p48 is essential for the formation of the exocrine and the correct spatial organization of the endocrine pancreas. Genes Dev. 1998; 12(23):3752-3763. (Biology). View Reference
-
Masui T, Swift GH, Hale MA, Meredith DM, Johnson JE, Macdonald RJ. Transcriptional autoregulation controls pancreatic Ptf1a expression during development and adulthood. Mol Cell Biol. 2008; 28(17):5458-5468. (Biology). View Reference
-
Nakhai H, Sel S, Favor J, et al. Ptf1a is essential for the differentiation of GABAergic and glycinergic amacrine cells and horizontal cells in the mouse retina. Development. 2007; 134:1151-1160. (Biology). View Reference
-
Pan FC, Bankaitis ED, Boyer D, et al. Spatiotemporal patterns of multipotentiality in Ptf1a-expressing cells during pancreas organogenesis and injury-induced facultative restoration. Development. 2013; 140(4):751-764. (Biology). View Reference
-
Roux E, Strubin M, Hagenbüchle O, Wellauer PK. The cell-specific transcription factor PTF1 contains two different subunits that interact with the DNA. Genes Dev. 1989; 3(10):1613-1624. (Biology). View Reference
-
Sellick GS, Barker KT, Stolte-Dijkstra I, et al. Mutations in PTF1A cause pancreatic and cerebellar agenesis. Nat Genet. 2004; 36(12):1301-1305. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical Data Sheets before using this product as described.
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.