Old Browser
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


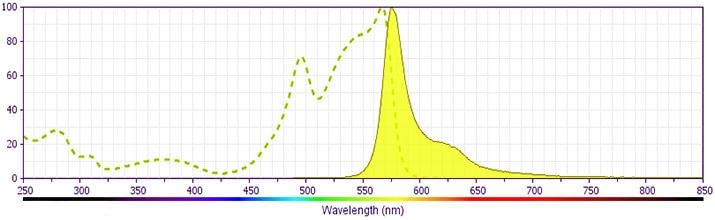
CD56 PE
Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
The antibody reagent is stable until the expiration date shown on the label when stored at 2° to 8°C. Do not use after the expiration date. Do not freeze the reagent or expose it to direct light during storage or incubation with cells. Keep the outside of the reagent vial dry.
Do not use the reagent if you observe any change in appearance. Precipitation or discoloration indicates instability or deterioration.
CD56 is intended for in vitro diagnostic use in the identification of cells expressing CD56 antigen, using a FACS™ brand flow cytometer. The flow cytometer must be equipped to detect light scatter and the appropriate fluorescence, and be equipped with appropriate analysis software for data acquisition and analysis. Refer to your instrument user’s guide for instructions.
Development References (16)
-
Centers for Disease Control. Update: universal precautions for prevention of transmission of human immunodeficiency virus, hepatitis B virus, and other bloodborne pathogens in healthcare settings. MMWR. 1988; 37:377-388. (Biology).
-
Clinical Applications of Flow Cytometry: Quality Assurance and Immunophenotyping of Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes. NCCLS document H42-T. 1992. (Biology).
-
Consensus protocol for the flow cytometric immunophenotyping of hematopoietic malignancies. Rothe G, Schmitz G. Leukemia. 1996; 10:877-895. (Biology).
-
Jackson AL, Warner NL. Rose NR, Friedman H, Fahey JL, ed. Manual of Clincial Laboratory Immunology, Third Edition. Washington DC: American Society for Microbiology; 1986:226-235.
-
Lanier LL, Chang C, Azuma M, Ruitenberg JJ, Hemperly JJ, Phillips JH. Molecular and functional analysis of human natural killer cell-associated neural cell adhesion molecule (N-CAM/CD56). J Immunol. 1991; 146(12):4421-4426. (Biology). View Reference
-
Lanier LL, Le AM, Civin CI, Loken MR, Phillips JH. The relationship of CD16 (Leu-11) and Leu-19 (NKH-1) antigen expression on human peripheral blood NK cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986; 136(12):4480-4486. (Biology). View Reference
-
Lanier LL, Testi R, Bindl J, Phillips JH. Identity of Leu-19 (CD56) leukocyte differentiation antigen and neural cell adhesion molecule. J Exp Med. 1989; 169(6):2233-2238. (Biology). View Reference
-
Loughran TP, Jr. Clonal diseases of large granular lymphocytes. Blood. 1993; 82:43844. (Biology).
-
Macon WR, Williams ME, Greer JP, et al. Natural killer-like T-cell lymphomas: aggressive lymphomas of T-large granular lymphocytes. Blood. 1996; 87:1474-1483. (Biology).
-
Nicholson J, Browning S, Orloff S, McDougal J. Inactivation of HIV-infected H9 cells in whole blood preparations by lysing/fixing reagents used in flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods. 1993; 160:215-218. (Biology).
-
Ocqueteau M, Orfao A, Almeida J, et al. Immunophenotypic characterization of plasma cells from monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance patients. Implications for the differential diagnosis between MGUS and multiple myeloma. Am J Pathol. 1998; 152:1655-1665. (Biology).
-
Okuno SH, Tefferi A, Hanson C, Katzmann JA, Li CY, Witzig TE. Spectrum of diseases associated with increased proportions or absolute numbers of peripheral blood natural killer cells. Br J Haematol. 1996; 93:810-812. (Biology).
-
Protection of Laboratory Workers from Infectious Disease Transmitted by Blood, Body Fluids, and Tissue: Tentative Guideline. NCCLS document M29-T2. (Biology).
-
Schubert J, Lanier LL, Schmidt RE. Knapp W, Dörken B, Gilks WR, et al, ed. Leucocyte Typing IV: White Cell Differentiation Antigens. New York, NY: Oxford University Press; 1989:699-702.
-
Stelzer GT, Marti G, Hurley A, McCoy PJ, Lovett EJ, Schwartz A. US-Canadian consensus recommendations on the immunophenotypic analysis of hematologic neoplasia by flow cytometry: standardization and validation of laboratory procedures. Cytometry. 1997; 30:214-230. (Biology).
-
Van Camp B, Durie BGM, Spier C, et al. Plasma cells in multiple myeloma express a natural killer cell-associated antigen: CD56 (NKH-1; Leu-19). Blood. 1990; 76:377-382. (Biology).
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For In Vitro Diagnostics Use.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.