Old Browser
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




Two-color flow cytometric analysis of CD23 expression on mouse splenocytes. Mouse splenic leucocytes were preincubated with Purified Rat Anti-Mouse CD16/CD32 antibody (Mouse BD Fc Block™) (Cat. No. 553141/553142). The cells were then stained with FITC Anti-Mouse IgM[a] antibody (Cat. No. 553516) and either BD Horizon™ BV711 Rat IgG2a, κ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 563047; Left Panel) or BD Horizon™ BV711 Rat Anti-Mouse CD23 antibody (Cat. No. 563987; Right Panel). Two-color flow cytometric dot plots show the correlated expression patterns of CD23 (or Ig Isotype control staining) versus IgM for gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of viable splenic leucocytes. Flow cytometric analysis was performed using a BD™ LSR II Flow Cytometer System.


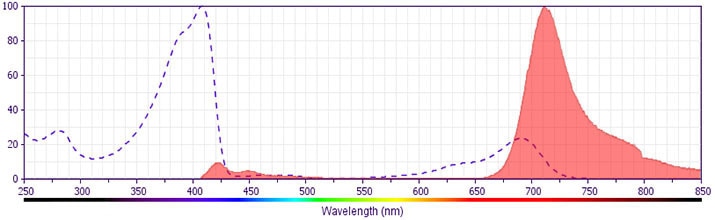
BD Horizon™ BV711 Rat Anti-Mouse CD23

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
For optimal and reproducible results, BD Horizon Brilliant™ Stain Buffer should be used anytime BD Horizon Brilliant™ dyes are used in a multicolor flow cytometry panel. Fluorescent dye interactions may cause staining artifacts which may affect data interpretation. The BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer was designed to minimize these interactions. When BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer is used in in the multicolor panel, it should also be used in the corresponding compensation controls for all dyes to achieve the most accurate compensation. For the most accurate compensation, compensation controls created with either cells or beads should be exposed to BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer for the same length of time as the corresponding multicolor panel. More information can be found in the Technical Data Sheet of the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer (Cat. No. 563794/566349) or the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer Plus (Cat. No. 566385).
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
- Alexa Fluor® is a registered trademark of Molecular Probes, Inc., Eugene, OR.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Cy is a trademark of GE Healthcare.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673; 8,158,444; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Violet 711 is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673; 8,158,444; 8,227,187; 8,455,613; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products






Development References (14)
-
Conrad DH, Waldschmidt TJ, Lee WT, et al. Effect of B cell stimulatory factor-1 (interleukin 4) on Fc epsilon and Fc gamma receptor expression on murine B lymphocytes and B cell lines. J Immunol. 1987; 139(7):2290-2296. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry, Functional assay, Immunoaffinity chromatography, Immunoprecipitation, Radioimmunoassay). View Reference
-
Coyle AJ, Wagner K, Bertrand C, Tsuyuki S, Bews J, Heusser C. Central role of immunoglobulin (Ig) E in the induction of lung eosinophil infiltration and T helper 2 cell cytokine production: inhibition by a non-anaphylactogenic anti-IgE antibody. J Exp Med. 1996; 183(4):1303-1310. (Clone-specific: Blocking). View Reference
-
Dasic G, Juillard P, Graber P, et al. Critical role of CD23 in allergen-induced bronchoconstriction in a murine model of allergic asthma. Eur J Immunol. 1999; 29(9):2957-2967. (Clone-specific: Blocking, In vivo exacerbation). View Reference
-
Kisselgof AB, Oettgen HC. The expression of murine B cell CD23, in vivo, is regulated by its ligand, IgE. Int Immunol. 1998; 10(9):1377-1384. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Maeda K, Burton GF, Padgett DA, et al. Murine follicular dendritic cells and low affinity Fc receptors for IgE (Fc epsilon RII). J Immunol. 1992; 148(8):2340-2347. (Clone-specific: Electron microscopy, Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
-
Oshiba A, Hamelmann E, Haczku A, et al. Modulation of antigen-induced B and T cell responses by antigen-specific IgE antibodies. J Immunol. 1997; 159(8):4056-4063. (Clone-specific: Blocking). View Reference
-
Pulendran B, Lingappa J, Kennedy MK, et al. Developmental pathways of dendritic cells in vivo: distinct function, phenotype, and localization of dendritic cell subsets in FLT3 ligand-treated mice. J Immunol. 1997; 159(5):2222-2231. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Rabin E, Cong YZ, Wortis HH. Loss of CD23 is a consequence of B-cell activation. Implications for the analysis of B-cell lineages. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992; 651:130-142. (Biology: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Rao M, Lee WT, Conrad DH. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody directed against the murine B lymphocyte receptor for IgE. J Immunol. 1987; 138(6):1845-1851. (Immunogen: Blocking, Immunoprecipitation, Inhibition, Radioimmunoassay). View Reference
-
Stief A, Texido G, Sansig G, et al. Mice deficient in CD23 reveal its modulatory role in IgE production but no role in T and B cell development. J Immunol. 1994; 152(7):3378-3390. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry, Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
-
Waldschmidt T, Snapp K, Foy T, Tygrett L, Carpenter C. B-cell subsets defined by the Fc epsilon R. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992; 651:84-98. (Biology). View Reference
-
Waldschmidt TJ, Conrad DH, Lynch RG. Expression of B cell surface receptors. II. IL-4 can accelerate the developmental expression of the murine B cell IgE Fc receptor. J Immunol. 1989; 143(9):2820-2827. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry, Immunoaffinity chromatography). View Reference
-
Waldschmidt TJ, Conrad DH, Lynch RG. The expression of B cell surface receptors. I. The ontogeny and distribution of the murine B cell IgE Fc receptor. J Immunol. 1988; 140(7):2148-2154. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Yu P, Kosco-Vilbois M, Richards M, Kohler G, Lamers MC. Negative feedback regulation of IgE synthesis by murine CD23. Nature. 1994; 369(6483):753-756. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.