Old Browser
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?






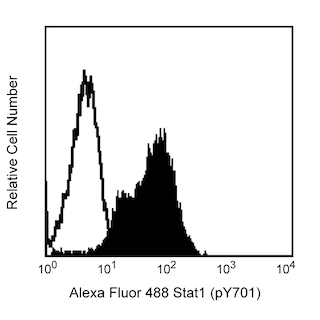
Flow cytometric analysis of H2AX (pS139) expression in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (left panel). Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells were either not treated (dashed line histogram) or cultured with 50 μM Etoposide (Calbiochem, Cat. No. 341205) for 2 hrs at 37°C (solid line histogram). The cells were fixed with BD Cytofix™ Fixation Buffer (Cat. No. 554655) and permeabilized with BD Phosflow™ Perm Buffer III (Cat. No.558050). After washing with BD Pharmingen™ Stain Buffer (FBS) (Cat. No. 554656), the cells were stained with BD Horizon™ BV421 Mouse Anti-H2AX (pS139) antibody (Cat. No. 564720). The fluorescence histograms were derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of intact lymphocytes. Flow cytometric analysis was performed using a BD™ LSR II Flow Cytometer System. Immunofluorescent analysis of H2AX expression by apoptotic human cells (right panel). HeLa cells (ATCC, CCL-2) were treated with camptothecin (20 µM, 6 hours) to induce apoptosis. Cells were then fixed with BD Cytofix™ Fixation Buffer (Cat. No. 554655), permeabilized with BD Phosflow™ Perm Buffer III (Cat. No. 558050), and blocked with 5% goat serum, 1% BSA, and 0.5% Triton™ X-100 diluted in PBS. Cells were stained with BD Horizon™ BV421 Mouse Anti-H2AX (pS139) antibody (Cat. No. 564720, pseudo-colored red) and Alexa Fluor® 488 Mouse Anti-Cytochrome c antibody (Cat. No. 560263, pseudo-colored green). DRAQ5 was used as a nuclear counterstain (Cat. No. 564902/564903, pseudo-colored blue). Images were captured on a standard epifluorescence microscope. Original magnification, 20x.

Immunofluorescent analysis of H2AX expression by apoptotic human cells. HeLa cells (ATCC, CCL-2) were treated with camptothecin (20 µM, 6 hours) to induce apoptosis. Cells were then fixed with BD Cytofix™ Fixation Buffer (Cat. No. 554655), permeabilized with BD Phosflow™ Perm Buffer III (Cat. No. 558050), and blocked with 5% goat serum, 1% BSA, and 0.5% Triton™ X-100 diluted in PBS. Cells were stained with BD Horizon™ BV421 Mouse Anti-H2AX (pS139) antibody (Cat. No. 564720, pseudo-colored red) and Alexa Fluor® 488 Mouse Anti-Cytochrome c antibody (Cat. No. 560263, pseudo-colored green). DRAQ5 was used as a nuclear counterstain (Cat. No. 564902/564903, pseudo-colored blue). Images were captured on a standard epifluorescence microscope. Original magnification, 20x.


BD Horizon™ BV421 Mouse Anti-H2AX (pS139)

BD Horizon™ BV421 Mouse Anti-H2AX (pS139)

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
For optimal and reproducible results, BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer should be used anytime two or more BD Horizon Brilliant dyes are used in the same experiment. Fluorescent dye interactions may cause staining artifacts which may affect data interpretation. The BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer was designed to minimize these interactions. More information can be found in the Technical Data Sheet of the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer (Cat. No. 563794).
Product Notices
- This reagent has been pre-diluted for use at the recommended Volume per Test. We typically use 1 × 10^6 cells in a 100-µl experimental sample (a test).
- Pacific Blue™ is a trademark of Molecular Probes, Inc., Eugene, OR.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673; 8,158,444; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Violet 421 is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,158,444; 8,362,193; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
- Alexa Fluor® is a registered trademark of Molecular Probes, Inc., Eugene, OR.
- Triton is a trademark of the Dow Chemical Company.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products




Histones are highly basic proteins that complex with DNA to form chromatin. The H2AX histone (~15 kDa calculated molecular weight) is a member of the H2A histone family whose members are components of nucleosomal histone octamers. Double-stranded breaks in DNA caused by replication errors, apoptosis, or other physiological processes (including, immunoglobulin and TCR gene recombinations) and DNA damage caused by ionizing radiation, UV light, or cytotoxic agents lead to phosphorylation of H2AX on serine 139. H2AX (pS139) is also referred to as H2AX (pS140) when the N-terminal methionine that is normally excised during posttranslational processing is included in amino acid sequence numbering. Kinases such as ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) or ATM-Rad3-related (ATR) phosphorylate H2AX to induce its function. Phosphorylated H2AX (also termed, gamma-H2AX) functions to recruit and localize DNA repair proteins or cell cycle checkpoint factors to the DNA-damaged sites. In this way, phosphorylated H2AX promotes DNA repair and maintains genomic stability and thus helps prevent oncogenic transformations.
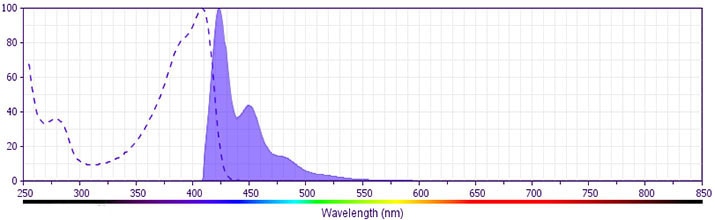
The antibody was conjugated to BD Horizon BV421 which is part of the BD Horizon Brilliant™ Violet family of dyes. With an Ex Max of 407-nm and Em Max at 421-nm, BD Horizon BV421 can be excited by the violet laser and detected in the standard Pacific Blue™ filter set (eg, 450/50-nm filter). BD Horizon BV421 conjugates are very bright, often exhibiting a 10 fold improvement in brightness compared to Pacific Blue conjugates.
Development References (7)
-
Austin WR, Armijo AL, Campbell DO, et al.. Nucleoside salvage pathway kinases regulate hematopoiesis by linking nucleotide metabolism with replication stress. J Exp Med. 2012; 209(12):2215-2228. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Burma S, Chen BP, Murphy M, Kurimasa A, Chen DJ. ATM phosphorylates histone H2AX in response to DNA double-strand breaks. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276(45):42462-42467. (Biology). View Reference
-
Fernandez-Capetillo O, Lee A, Nussenzweig M, Nussenzweig A. H2AX: the histone guardian of the genome. DNA Repair (Amst). 2004; 3(8-9):959-967. (Biology). View Reference
-
Kuo LJ, Yang LX. Gamma-H2AX - A novel biomarker for DNA double-strand breaks. In Vivo. 2008; 22(3):305-309. (Biology). View Reference
-
Lavelle D, Vaitkus K, Ling Y, et al. Effects of tetrahydrouridine on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of oral decitabine. Blood. 2012; 119(5):1240-1247. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Rogakou EP, Nieves-Neira W, Boon C, Pommier Y, Bonner WM. Initiation of DNA fragmentation during apoptosis induces phosphorylation of H2AX histone at serine 139. J Biol Chem. 2000; 275(13):9390-9395. (Biology). View Reference
-
Rogakou EP, Pilch DR, Orr AH, Ivanova VS, Bonner WM. DNA double-stranded breaks induce histone H2AX phosphorylation on serine 139. J Biol Chem. 1998; 273(10):5858-5868. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.