Old Browser
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




Multicolor flow cytometric analysis of mouse splenic dendritic cells. C57BL/6 mouse splenic leucocytes were preincubated with Purified Rat Anti-Mouse CD16/CD32 antibody (Mouse BD Fc Block™) (Cat. No. 553141/553142). The cells were then stained with APC Rat Anti-Mouse CD11b (Cat. No. 553312/561690) and BV421 Hamster Anti-Mouse CD11c (Cat. No. 562782) antibodies, and either BD Horizon BB515™ Rat IgG2b, κ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 564421; dashed line histograms) or BD Horizon BB515 Rat Anti-Mouse Dendritic Cells antibody (Cat. No. 565171; solid line histograms). The fluorescence histogram showing Dendritic Cells antigen expression (or Ig Isotype control staining) were derived from either CD11b+ CD11c- (Left Panel) or CD11b [intermediate] CD11c+ (Right Panel) gated events, as indicated, with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of intact leucocytes. Flow cytometric analysis was performed using a BD LSRFortessa™ Cell Analyzer System.


BD Horizon™ BB515 Rat Anti-Mouse Dendritic Cells

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
BD™ CompBeads can be used as surrogates to assess fluorescence spillover (Compensation). When fluorochrome conjugated antibodies are bound to CompBeads, they have spectral properties very similar to cells. However, for some fluorochromes there can be small differences in spectral emissions compared to cells, resulting in spillover values that differ when compared to biological controls. It is strongly recommended that when using a reagent for the first time, users compare the spillover on cells and CompBead to ensure that BD Comp beads are appropriate for your specific cellular application.
For optimal and reproducible results, BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer should be used anytime two or more BD Horizon Brilliant dyes are used in the same experiment. Fluorescent dye interactions may cause staining artifacts which may affect data interpretation. The BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer was designed to minimize these interactions. More information can be found in the Technical Data Sheet of the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer (Cat. No. 563794/566349) or the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer Plus (Cat. No. 566385).
For optimal results, it is recommended to perform 2 washes after staining with antibodies. Cells may be prepared, stained with antibodies and washed twice with wash buffer per established protocols for immunofluorescence staining, prior to acquisition on a flow cytometer. Performing fewer than the recommended wash steps may lead to increased spread of the negative population.
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to http://regdocs.bd.com to access safety data sheets (SDS).
- BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673; 8,158,444; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products






The 33D1 antibody recognizes Dendritic cell inhibitory receptor 2 (Dcir2) which is also known as, Dendritic Cells antigen, Dendritic Cell (DC) Marker, or 33D1 antigen. This antigen is expressed on most dendritic cells of spleen, lymph node, and Peyer's patch, but not liver, bone marrow, or epidermal dendritic cells; macrophages; other leukocytes; or erythroid cells. Within the spleen, the majority of 33D1+ DC are localized in the marginal zones. Thymic dendritic cells may express a low level of the 33D1 Antigen. It has been reported that bone-marrow DC can be induced to express the 33D1 antigen by culture in the presence of GM-CSF, and the resulting 33D1+ DC are effective in in vitro (induction of MLR) and in vivo (anti-tumoral vaccination) assays for antigen presentation. However, the addition of IL-4 to GM-CSF in bone-marrow cultures resulted in loss of 33D1 expression and enhanced the MLR-stimulatory activity of the DC. It has also been reported that 33D1 expression is upregulated when liver-derived DC are cultured on collagen-coated plates in the presence of GM-CSF. In vivo functional 33D1+ DC are induced in the brains of mice chronically infected with Toxoplasma gondii, probably via the parasite's induction of GM-CSF.
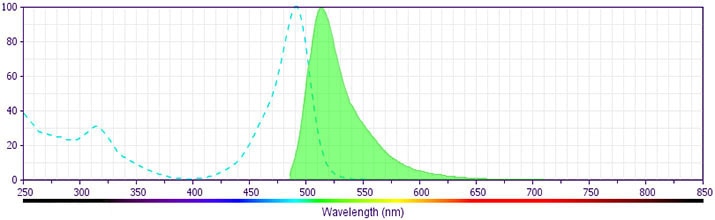
The antibody was conjugated to BD Horizon BB515 which is part of the BD Horizon Brilliant™ Blue family of dyes. With an Ex Max near 490 nm and an Em Max near 515 nm, BD Horizon BB515 can be excited by the blue laser (488 nm) laser and detected with a 530/30 nm filter. This dye has been exclusively developed by BD Biosciences and is up to seven times brighter than FITC with less spillover into the PE channel. Due to similar excitation and emission properties, BB515, FITC, and Alexa Fluor® 488 cannot be used simultaneously. It is not recommended to use BB515 in cocktails that include Streptavidin conjugates as it may cause high background.
Development References (13)
-
Crowley M, Inaba K, Witmer-Pack M, Steinman RM. The cell surface of mouse dendritic cells: FACS analyses of dendritic cells from different tissues including thymus. Cell Immunol. 1989; 118(1):108-125. (Biology). View Reference
-
Dudziak D, Kamphorst AO, Nussenzweig MC, et al. Differential antigen processing by dendritic cell subsets in vivo. Science. 2007; 315(5808):107-111. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Fischer HG, Bonifas U, Reichmann G. Phenotype and functions of brain dendritic cells emerging during chronic infection of mice with Toxoplasma gondii. J Immunol. 2000; 164(9):4826-4834. (Biology). View Reference
-
Inaba K, Inaba M, Romani N, et al. Generation of large numbers of dendritic cells from mouse bone marrow cultures supplemented with granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Exp Med. 1992; 176(6):1693-1702. (Biology). View Reference
-
Kelsall BL, Strober W. Distinct populations of dendritic cells are present in the subepithelial dome and T cell regions of the murine Peyer's patch. J Exp Med. 1996; 183(1):237-247. (Biology). View Reference
-
Lu L, Woo J, Rao AS, et al. Propagation of dendritic cell progenitors from normal mouse liver using granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor and their maturational development in the presence of type-1 collagen. J Exp Med. 1994; 179(6):1823-1834. (Biology). View Reference
-
Masurier C, Pioche-Durieu C, Colombo BM, et al. Immunophenotypical and functional heterogeneity of dendritic cells generated from murine bone marrow cultured with different cytokine combinations: implications for anti-tumoral cell therapy. Immunology. 1999; 96(4):569-577. (Biology). View Reference
-
Nussenzweig MC, Steinman RM, Witmer MD, Gutchinov B. A monoclonal antibody specific for mouse dendritic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982; 79(1):161-165. (Immunogen: Cytotoxicity, Depletion, Radioimmunoassay). View Reference
-
Pulendran B, Lingappa J, Kennedy MK, et al. Developmental pathways of dendritic cells in vivo: distinct function, phenotype, and localization of dendritic cell subsets in FLT3 ligand-treated mice. J Immunol. 1997; 159(5):2222-2231. (Biology). View Reference
-
Steinman RM, Gutchinov B, Witmer MD, Nussenzweig MC. Dendritic cells are the principal stimulators of the primary mixed leukocyte reaction in mice. J Exp Med. 1983; 157(2):613-627. (Biology). View Reference
-
Vremec D, Zorbas M, Scollay R, et al. The surface phenotype of dendritic cells purified from mouse thymus and spleen: investigation of the CD8 expression by a subpopulation of dendritic cells. J Exp Med. 1992; 176(1):47-58. (Biology). View Reference
-
Witmer MD, Steinman RM. The anatomy of peripheral lymphoid organs with emphasis on accessory cells: light-microscopic immunocytochemical studies of mouse spleen, lymph node, and Peyer's patch. Am J Anat. 1984; 170(3):465-481. (Biology). View Reference
-
Woo J, Lu L, Rao AS, et al. Isolation, phenotype, and allostimulatory activity of mouse liver dendritic cells. Transplantation. 1994; 58(4):484-491. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.