Old Browser
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




Two-color flow cytometric analysis of CD71 expression on developing mouse erythroid cells. BALB/c mouse bone marrow cells were stained with PE Rat Anti-Mouse TER-119/Erythroid Cells antibody (Cat. No. 553673/561071) and either BD Horizon™ BV605 Rat IgG1, κ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 562993, Left Panel) or BD Horizon™ BV605 Rat Anti-Mouse CD71 (Cat. No. 563013, Right Panel). The two-color flow cytometric dot plots show the correlated expression of CD71 (or Ig Isotype control staining) versus TER-119 for gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of viable bone marrow cells. Flow cytometry was performed using a BD™ LSR II Flow Cytometer System


BD Horizon™ BV605 Rat Anti-Mouse CD71

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Please observe the following precautions: Absorption of visible light can significantly alter the energy transfer occurring in any tandem fluorochrome conjugate; therefore, we recommend that special precautions be taken (such as wrapping vials, tubes, or racks in aluminum foil) to prevent exposure of conjugated reagents, including cells stained with those reagents, to room illumination.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Although every effort is made to minimize the lot-to-lot variation in the efficiency of the fluorochrome energy transfer, differences in the residual emission from BD Horizon™ BV421 may be observed. Therefore, we recommend that individual compensation controls be performed for every BD Horizon™ BV605 conjugate.
- CF™ is a trademark of Biotium, Inc.
Companion Products



.png?imwidth=320)
.png?imwidth=320)
The C2 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to CD71, the transferrin receptor. CD71 is a disulfide-linked homodimer of 95-kDa subunits. CD71 mediates one of the cellular mechanisms for iron uptake, and its expression is regulated according to the cell's iron requirements. It is expressed at high levels on developing erythroid cells, and it is upregulated after mitogenic activation of B or T lymphocytes. The C2 monoclonal antibody selectivity inhibits some types of T- and B-cell activation by down-regulation of transferrin receptor expression, but it does not block binding of transferrin.
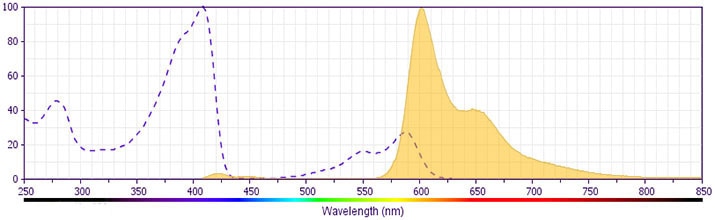
This antibody is conjugated to BD Horizon BV605 which is part of the BD Horizon Brilliant™ Violet family of dyes. With an Ex Max of 407-nm and Em Max of 602-nm, BD Horizon BV605 can be excited by a violet laser and detected with a standard 610/20-nm filter set. BD Horizon BV605 is a tandem fluorochrome of BD Horizon BV421 and an acceptor dye with an Em max at 605-nm. Due to the excitation of the acceptor dye by the green (532 nm) and yellow-green (561 nm) lasers, there will be significant spillover into the PE and BD Horizon PE-CF594 detectors off the green or yellow-green lasers. BD Horizon BV605 conjugates are very bright, often exhibiting brightness equivalent to PE conjugates and can be used as a third color off of the violet laser.
For optimal and reproducible results, BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer should be used anytime two or more BD Horizon Brilliant dyes are used in the same experiment. Fluorescent dye interactions may cause staining artifacts which may affect data interpretation. The BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer was designed to minimize these interactions. More information can be found in the Technical Data Sheet of the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer (Cat. No. 563794).
Development References (5)
-
Fujimoto T. GPI-anchored proteins, glycosphingolipids, and sphingomyelin are sequestered to caveolae only after crosslinking. J Histochem Cytochem. 1996; 44(8):929-941. (Clone-specific: Immunofluorescence). View Reference
-
Kemp JD, Thorson JA, Gomez F, Smith KM, Cowdery JS, Ballas ZK. Inhibition of lymphocyte activation with anti-transferrin receptor Mabs: a comparison of three reagents and further studies of their range of effects and mechanism of action. Cell Immunol. 1989; 122(1):218-230. (Clone-specific: Activation, Inhibition). View Reference
-
Kemp JD, Thorson JA, McAlmont TH, Horowitz M, Cowdery JS, Ballas ZK. Role of the transferrin receptor in lymphocyte growth: a rat IgG monoclonal antibody against the murine transferrin receptor produces highly selective inhibition of T and B cell activation protocols. J Immunol. 1987; 138(8):2422-2426. (Immunogen: Activation, Immunoprecipitation, Inhibition). View Reference
-
Lok CN, Loh TT. Regulation of transferrin function and expression: review and update. Biol Signals Recept. 1998; 7(3):157-178. (Biology). View Reference
-
Thorson JA, Smith KM, Gomez F, Naumann PW, Kemp JD. Role of iron in T cell activation: TH1 clones differ from TH2 clones in their sensitivity to inhibition of DNA synthesis caused by IgG Mabs against the transferrin receptor and the iron chelator deferoxamine. Cell Immunol. 1991; 134(1):126-137. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.