-
Training
- Flow Cytometry Basic Training
-
Product-Based Training
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter Product Training
- Accuri C6 Plus Product-Based Training
- FACSAria Product Based Training
- FACSCanto Product-Based Training
- FACSLyric Product-Based Training
- FACSMelody Product-Based Training
- FACSymphony Product-Based Training
- HTS Product-Based Training
- LSRFortessa Product-Based Training
- Advanced Training
-
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter Product Training
- Accuri C6 Plus Product-Based Training
- FACSAria Product Based Training
- FACSCanto Product-Based Training
- FACSLyric Product-Based Training
- FACSMelody Product-Based Training
- FACSymphony Product-Based Training
- HTS Product-Based Training
- LSRFortessa Product-Based Training
- United States (English)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




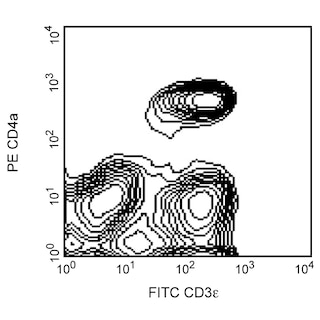
Flow cytometric analysis of CD8 expression on pig peripheral blood lymphocytes. Pig whole blood was stained simultaneously with PE Mouse Anti-Pig CD4a antibody (Cat. No. 559586) and Alexa Fluor® 647 Mouse Anti-Pig CD8a antibody (Cat. no. 561475). The erythrocytes were lysed with BD PharmLyse™ Lysing Buffer (Cat. No. 555899). The two-color flow cytometric dot plot shows the expression of CD8 versus CD4 derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of viable lymphocytes. Flow cytometry was performed using a BD™ LSR II Flow Cytometer System.


BD Pharmingen™ Alexa Fluor® 647 Mouse Anti-Pig CD8a

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- The Alexa Fluor®, Pacific Blue™, and Cascade Blue® dye antibody conjugates in this product are sold under license from Molecular Probes, Inc. for research use only, excluding use in combination with microarrays, or as analyte specific reagents. The Alexa Fluor® dyes (except for Alexa Fluor® 430), Pacific Blue™ dye, and Cascade Blue® dye are covered by pending and issued patents.
- Alexa Fluor® is a registered trademark of Molecular Probes, Inc., Eugene, OR.
- Alexa Fluor® 647 fluorochrome emission is collected at the same instrument settings as for allophycocyanin (APC).
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
Companion Products


The 76-2-11 (also known as clone PT8) monoclonal antibody specifically binds to an epitope on the CD8α chain, a 35-kDa antigen expressed on thymocytes, peripheral T lymphocytes, and NK cells. The CD8 molecule can exist as a 70 kDa homodimer, composed of α chains, or heterodimer, composed of an α and β chain. Cells which express the CD8αα homodimer display dimmer staining with mAb 76-2-11 than CDαβ-expressing cells. The 76-2-11 mAb does not cross-react with human or bovine cells. Two peripheral CD8+ T-cell populations can be distinguished in the pig: CD8-bright CD4- CTL effectors/precursors and CD8-dull CD4+ T-helper lymphocytes. Pig NK cells express CD8 (dull staining), CD2, MHC class II, LFA-1, and asialo-GM1, but not CD3, CD4, CD5, or CD6. mAb 76-2-11 has been reported to partially inhibit in vitro cytotoxic activity of PBL to allogeneic leukocytes, but not NK-cell-mediated lysis, and to deplete CD8+ T cells in vivo. This clone was clustered as anti-CD8a at the First International Swine CD workshop.
Development References (13)
-
Dato ME, Kim YB. Characterization and utilization of a monoclonal antibody inhibiting porcine natural killer cell activity for isolation of natural killer and killer cells. J Immunol. 1990; 144(11):4452-4462. (Biology). View Reference
-
Pescovitz MD, Lowman MA, Sachs DH. Expression of T-cell associated antigens by porcine natural killer cells. Immunology. 1988; 65(2):267-271. (Biology). View Reference
-
Pescovitz MD, Lunney JK, Sachs DH. Murine anti-swine T4 and T8 monoclonal antibodies: distribution and effects on proliferative and cytotoxic T cells. J Immunol. 1985; 134(1):37-44. (Biology). View Reference
-
Pescovitz MD, Lunney JK, Sachs DH. Preparation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies reactive with porcine PBL. J Immunol. 1984; 133(1):368-375. (Immunogen). View Reference
-
Saalmuller A, Aasted B, Canals A, et al. Analyses of mAb reactive with porcine CD8. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1994; 43(1-3):249-254. (Clone-specific). View Reference
-
Saalmuller A, Hirt W, Maurer S, Weiland E. Discrimination between two subsets of porcine CD8+ cytolytic T lymphocytes by the expression of CD5 antigen. Immunology. 1994; 81(4):578-583. (Biology). View Reference
-
Saalmuller A, Pauly T, Hohlich BJ, Pfaff E. Characterization of porcine T lymphocytes and their immune response against viral antigens. J Biotechnol. 1999; 73(2-3):223-233. (Biology). View Reference
-
Saalmuller A, Werner T, Fachinger V. T-helper cells from naive to committed. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2002; 87(3-4):137-145. (Biology). View Reference
-
Smith CV, Sablinski T, Arn JS, et al. In vivo treatment with monoclonal antibodies directed against CD4 and CD8 antigens in miniature swine. J Immunother Emphasis Tumor Immunol. 1994; 16(2):105-114. (Biology). View Reference
-
Suzuki T, Sundt TM 3rd, Mixon A, Sachs DH. In vivo treatment with antiporcine T cell antibodies. Transplantation. 1990; 50(1):76-81. (Biology). View Reference
-
Waters WR, Hontecillas R, Sacco RE, et al. Antigen-specific proliferation of porcine CD8alphaalpha cells to an extracellular bacterial pathogen. Immunology. 2000; 101(3):333-341. (Clone-specific). View Reference
-
Zuckermann FA, Pescovitz MD, Aasted B, et al. Report on the analyses of mAb reactive with porcine CD8 for the second international swine CD workshop. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1998; 60(3-4):291-303. (Clone-specific). View Reference
-
Zuckermann FA. Extrathymic CD4/CD8 double positive T cells. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1999; 72(1-2):55-66. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.