-
Your selected country is
Middle East / Africa
- Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
BD™ CompBeads can be used as surrogates to assess fluorescence spillover (Compensation). When fluorochrome conjugated antibodies are bound to BD CompBeads, they have spectral properties very similar to cells. However, for some fluorochromes there can be small differences in spectral emissions compared to cells, resulting in spillover values that differ when compared to biological controls. It is strongly recommended that when using a reagent for the first time, users compare the spillover on cells and BD CompBead to ensure that BD CompBeads are appropriate for your specific cellular application.
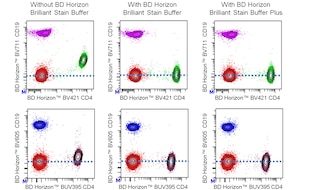
For optimal and reproducible results, BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer should be used anytime two or more BD Horizon Brilliant dyes are used in the same experiment. Fluorescent dye interactions may cause staining artifacts which may affect data interpretation. The BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer was designed to minimize these interactions. More information can be found in the Technical Data Sheet of the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer (Cat. No. 563794/566349) or the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer Plus (Cat. No. 566385).
Note: When using high concentrations of antibody, background binding of this dye to erythroid cell subsets (mature erythrocytes and precursors) has been observed. For researchers studying these cell populations, or in cases where light scatter gating does not adequately exclude these cells from the analysis, this background may be an important factor to consider when selecting reagents for panel(s).
Product Notices
- The production process underwent stringent testing and validation to assure that it generates a high-quality conjugate with consistent performance and specific binding activity. However, verification testing has not been performed on all conjugate lots.
- Researchers should determine the optimal concentration of this reagent for their individual applications.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673; 8,158,444; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
- Please refer to http://regdocs.bd.com to access safety data sheets (SDS).
- CF™ is a trademark of Biotium, Inc.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Ultraviolet 615 is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673; 8,158,444; 8,227,187; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
Companion Products
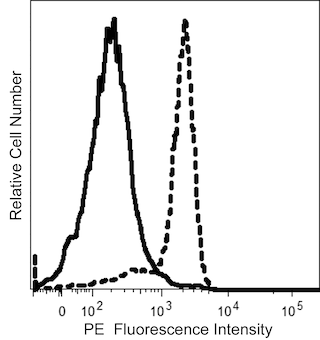




The L60 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to CD43 which is also known as Leukosialin (LSN) or Galactoglycoprotein (GALGP). CD43 is a ~95-135 kDa heavily O-sialylated type I transmembrane glycoprotein that is encoded by SPN (sialophorin) and belongs to the cell surface mucin family. The L60 antibody recognizes a sialic acid-dependent determinant on CD43. CD43 is highly expressed on T lymphocytes, thymocytes, monocytes, granulocytes, bone marrow stem cells, pre-B cells and activated B cells plasma cells but not on resting peripheral blood B cells, red blood cells, and non-hematopoietic cells. CD43 is enzymatically shed from leucocyte surfaces following activation by various stimuli. CD43 appears to be involved in mediating intercellular interactions that regulate leucocyte functions.
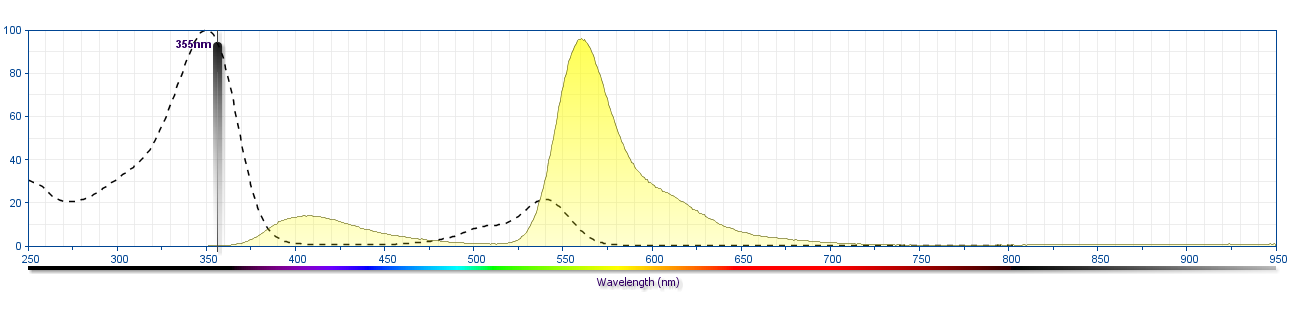
The antibody was conjugated to BD Horizon BUV615 which is part of the BD Horizon Brilliant™ Ultraviolet family of dyes. This dye is a tandem fluorochrome with an Ex Max near 350 nm and an Em Max near 615 nm. BD Horizon Brilliant BUV615 can be excited by the ultraviolet laser (355 nm) and detected with a 610/20 filter and a 595 nm LP. Due to the excitation of the acceptor dye by the blue/yellow-green laser line, there may be significant spillover into channels detecting PE-CF594 like emissions (eg, 610/20-nm filter).
Development References (15)
-
Ardman B, Sikorski MA, Staunton DE. CD43 interferes with T-lymphocyte adhesion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 June; 89(11):5001-5005. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry, Functional assay, Immunoprecipitation, Radioimmunoassay). View Reference
-
Bazil V, Strominger JL. CD43, the major sialoglycoprotein of human leukocytes, is proteolytically cleaved from the surface of stimulated lymphocytes and granulocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May; 90(9):3792-3796. (Biology). View Reference
-
Campanero MR, Pulido R, Alonso JL, et al. Down-regulation by tumor necrosis factor-alpha of neutrophil cell surface expression of the sialophorin CD43 and the hyaluronate receptor CD44 through a proteolytic mechanism. Eur J Immunol. 1991 December; 21(12):3045-3048. (Biology). View Reference
-
Cyster JG, Williams AF. The importance of cross-linking in the homotypic aggregation of lymphocytes induced by anti-leukosialin (CD43) antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1992 October; 22(10):2565-2572. (Biology). View Reference
-
Kuijpers TW, Hoogerwerf M, Kuijpers KC, Schwartz BR, Harlan JM. Cross-linking of sialophorin (CD43) induces neutrophil aggregation in a CD18-dependent and a CD18-independent way. J Immunol. 1992 August; 149(3):998-1003. (Biology). View Reference
-
Ngan BY, Picker LJ, Medeiros LJ, Warnke RA. Immunophenotypic diagnosis of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma in paraffin sections. Co-expression of L60 (Leu-22) and L26 antigens correlates with malignant histologic findings.. Am J Clin Pathol. 1989; 91(5):579-83. (Clone-specific: Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
-
Park JK, Rosenstein YJ, Remold-O'Donnell E, Bierer BE, Rosen FS, Burakoff SJ. Enhancement of T-cell activation by the CD43 molecule whose expression is defective in Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. Nature. 1991 April; 350(6320):706-709. (Biology). View Reference
-
Rieu P, Porteu F, Bessou G, Lesavre P, Halbwachs-Mecarelli L. Human neutrophils release their major membrane sialoprotein, leukosialin (CD43), during cell activation. Eur J Immunol. 1992 November; 22(11):3021-3026. (Biology). View Reference
-
Rosenstein Y, Park JK, Hahn WC, Rosen FS, Bierer BE, Burakoff SJ. CD43, a molecule defective in Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, binds ICAM-1.. Nature. 1991; 354(6350):233-5. (Biology). View Reference
-
Segal GH, Stoler MH, Tubbs RR. The "CD43 only" phenotype. An aberrant, nonspecific immunophenotype requiring comprehensive analysis for lineage resolution. Am J Clin Pathol. 1992 June; 97(6):861-865. (Biology). View Reference
-
Stefanova I, Hilgert I, and Horejsi V. Studies of the CD43 panel antibodies. In: Knapp W. W. Knapp .. et al., ed. Leucocyte typing IV : white cell differentiation antigens. Oxford New York: Oxford University Press; 1989:608.
-
Stoll M, Dalchau R, Schmidt RE. Cluster report: CD43. In: Knapp W. W. Knapp .. et al., ed. Leucocyte typing IV : white cell differentiation antigens. Oxford New York: Oxford University Press; 1989:604-608.
-
Stross WP, Flavell DJ, Flavell SU, et al. Epitope specificity and staining properties of CD43 (sialophorin) antibodies. In: Knapp W. W. Knapp .. et al., ed. Leucocyte typing IV : white cell differentiation antigens. Oxford New York: Oxford University Press; 1989:615.
-
Stross WP, Warnke RA, Flavell DJ, et al. Molecule detected in formalin fixed tissue by antibodies MT1, DF-T1, and L60 (Leu-22) corresponds to CD43 antigen.. J Clin Pathol. 1989; 42(9):953-61. (Clone-specific: Western blot). View Reference
-
Wieczorek R, Buck D, Bindl J, Knowles DM. Monoclonal antibody Leu-22 (L60) permits the demonstration of some neoplastic T cells in routinely fixed and paraffin-embedded tissue sections.. Hum Pathol. 1988; 19(12):1434-43. (Immunogen: Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.