-
Your selected country is
Middle East / Africa
- Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




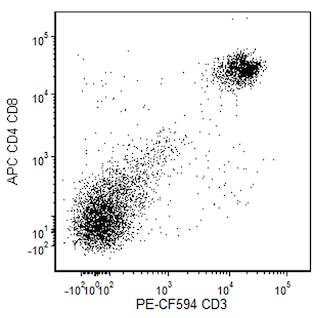
Flow Cytometric Analysis of CD62L Expression Left Panels - Flow cytometric analysis of CD62L expression on mouse bone marrow cells. Mouse bone marrow cells were left untreated (Left Panel) or were cultured (1 hour) with Phorbol 12-Myristate 13-Acetate (PMA; Middle Left Panel). The cells were preincubated with Purified Rat Anti-Mouse CD16/CD32 antibody (Mouse BD Fc Block™) (Cat. No. 553141/553142). The cells were then stained with either BD Horizon™ BV650 Rat IgG2a, κ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 563236, dashed line histogram) or BD Horizon BV650 Rat Anti-Mouse CD62L antibody (Cat. No. 564108, solid line histogram). Fluorescence histograms were derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of viable bone marrow cells. Flow cytometric analysis was performed using a BD™ LSR II Flow Cytometer System. Right Panels - Two-color flow cytometric analysis of CD62L expression on mouse splenocytes. Mouse splenic leucocytes were preincubated with Purified Rat Anti-Mouse CD16/CD32 antibody (Mouse BD Fc Block™). The cells then were stained with BD Horizon™ PE-CF594 Hamster Anti-Mouse CD3e antibody (Cat. No. 562286/562332) and either BD Horizon BV650 Rat IgG2a, κ Isotype Control (Middle Right Panel) or BD Horizon BV650 Rat Anti-Mouse CD62L antibody (Right Panel). Two-color contour plots showing the expression of CD62L (or Ig Isotype control staining) versus CD3e were derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of viable leucocytes. Flow cytometric analysis was performed using a BD™ LSR II Flow Cytometer System.


BD Horizon™ BV650 Rat Anti-Mouse CD62L

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
- Alexa Fluor® is a registered trademark of Molecular Probes, Inc., Eugene, OR.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products





The MEL-14 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to CD62L (L-selectin), a 95 kDa (on neutrophils) or 74 kDa (on lymphocytes) receptor with lectin-like and Epidermal Growth Factor-like domains. In the mouse, L-selectin is detected on most thymocytes, with the highest levels of expression on an immunocompetent subset and a population of dividing progenitor cells, and on peripheral leukocytes, including subsets of B and T lymphocytes, neutrophils, monocytes, and eosinophils. This member of the selectin adhesion molecule family appears to be required for lymphocyte homing to peripheral lymph nodes and to contribute to neutrophil emigration at inflammatory sites. L-selectin is rapidly shed from lymphocytes and neutrophils upon cellular activation; metalloproteinases may mediate the release of CD62L ectodomains from the cell surface. The level of CD62L expression, along with other markers, distinguishes naive, effector, and memory T cells. L-selectin binds to sialytaed oligosaccharide determinants on high endothelial venules (HEV) in peripheral lymph nodes. In vitro studies have demonstrated that CD34, GlyCAM-1, and MAdCAM-1, all recognized by mAb MECA-79 (anti-mouse PNAd Carbohydrate Epitope, Cat. No. 553863), may be ligands for CD62L. MEL-14 mAb blocks in vitro binding of lymphocytes to peripheral lymph node HEV and inhibits in vivo lymphocyte extravasation into peripheral lymph nodes and late stages of leukocyte rolling.
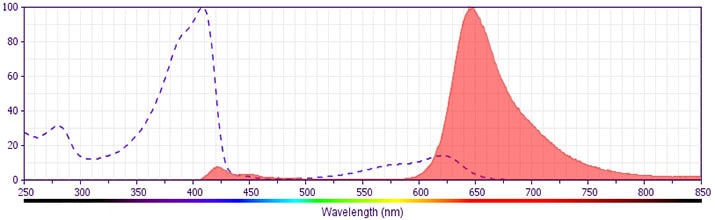
The antibody was conjugated to BD Horizon™ BV650 which is part of the BD Horizon Brilliant™ Violet family of dyes. This dye is a tandem fluorochrome of BD Horizon BV421 with an Ex Max of 405-nm and an acceptor dye with an Em Max at 650-nm. BD Horizon BV650 can be excited by the violet laser and detected in a filter used to detect APC-like dyes (eg, 660/20-nm filter). Due to the excitation and emission characteristics of the acceptor dye, there will be spillover into the APC and Alexa Fluor® 700 detectors. However, the spillover can be corrected through compensation as with any other dye combination.
Development References (16)
-
Cerwenka A, Carter LL, Reome JB, Swain SL, Dutton RW. In vivo persistence of CD8 polarized T cell subsets producing type 1 or type 2 cytokines. J Immunol. 1998; 161(1):97-105. (Clone-specific: Blocking, Flow cytometry, Immunoaffinity chromatography, Immunoprecipitation). View Reference
-
Ernst DN, Weigle WO, Noonan DJ, McQuitty DN, Hobbs MV. The age-associated increase in IFN-γ synthesis by mouse CD8+ T cells correlates with shifts in the frequencies of cell subsets defined by membrane CD44, CD45RB, 3G11, and MEL-14 expression. J Immunol. 1993; 151(2):575-587. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Gallatin WM, Weissman IL, Butcher EC. A cell-surface molecule involved in organ-specific homing of lymphocytes. Nature. 1983; 304(5921):30-34. (Immunogen: Blocking). View Reference
-
Iwabuchi K, Ohgama J, Ogasawara K, et al. Distribution of MEL-14+ cells in various lymphoid tissues. Immunobiology. 1991; 182(2):161-173. (Clone-specific: Cytotoxicity). View Reference
-
Jung TM, Gallatin WM, Weissman IL, Dailey MO. Down-regulation of homing receptors after T cell activation. J Immunol. 1988; 141(12):4110-4117. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Kishimoto TK, Jutila MA, Berg EL, Butcher EC. Neutrophil Mac-1 and MEL-14 adhesion proteins inversely regulated by chemotactic factors. Science. 1989; 245(4923):1238-1241. (Clone-specific: Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
-
Lewinsohn DM, Bargatze RF, Butcher EC. Leukocyte-endothelial cell recognition: evidence of a common molecular mechanism shared by neutrophils, lymphocytes, and other leukocytes. J Immunol. 1987; 138(12):4313-4321. (Clone-specific: Blocking, Immunoprecipitation). View Reference
-
Ley K, Bullard DC, Arbones ML, et al. Sequential contribution of L- and P-selectin to leukocyte rolling in vivo. J Exp Med. 1995; 181(2):669-675. (Clone-specific: Blocking). View Reference
-
Mobley JL, Dailey MO. Regulation of adhesion molecule expression by CD8 T cells in vivo. I. Differential regulation of gp90MEL-14 (LECAM-1), Pgp-1, LFA-1, and VLA-4 alpha during the differentiation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes induced by allografts. J Immunol. 1992; 148(8):2348-2356. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Pizcueta P, Luscinskas FW. Monoclonal antibody blockade of L-selectin inhibits mononuclear leukocyte recruitment to inflammatory sites in vivo. Am J Pathol. 1994; 145(2):461-469. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry, Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
-
Reichert RA, Jerabek L, Gallatin WM, Butcher EC, Weissman IL. Ontogeny of lymphocyte homing receptor expression in the mouse thymus. J Immunol. 1986; 136(10):3535-3542. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry, Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
-
Reichert RA, Weissman IL, Butcher EC. Dual immunofluorescence studies of cortisone-induced thymic involution: evidence for a major cortical component to cortisone-resistant thymocytes. J Immunol. 1986; 136(10):3529-3534. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Reichert RA, Weissman IL, Butcher EC. Phenotypic analysis of thymocytes that express homing receptors for peripheral lymph nodes. J Immunol. 1986; 136(10):3521-3528. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Siegelman MH, Cheng IC, Weissman IL, Wakeland EK. The mouse lymph node homing receptor is identical with the lymphocyte cell surface marker Ly-22: role of the EGF domain in endothelial binding. Cell. 1990; 61(4):611-622. (Clone-specific: Blocking, Immunoprecipitation). View Reference
-
Vestweber D. Ligand-specificity of the selectins. J Cell Biochem. 1996; 61(4):585-591. (Biology). View Reference
-
Yang G, Mizuno MT, Hellstrom KE, Chen L. B7-negative versus B7-positive P815 tumor: differential requirements for priming of an antitumor immune response in lymph nodes. J Immunol. 1997; 158(2):851-858. (Clone-specific: Blocking). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.