-
Your selected country is
Middle East / Africa
- Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




Flow cytometric analysis of NKB1 (CD158e1) expression on human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Whole blood was stained with FITC Mouse Anti-Human NKB1 (CD158e1) (Cat. No. 555966) and PE Mouse Anti-Human CD56 (Cat. No.555516/561903). Erythrocytes were lysed with BD FACS Lysing Solution (Cat. No. 555899).The fluorescence dot plot was derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scattering characteristics of viable lymphocytes.


BD Pharmingen™ FITC Mouse Anti-Human NKB1

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- This reagent has been pre-diluted for use at the recommended Volume per Test. We typically use 1 × 10^6 cells in a 100-µl experimental sample (a test).
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to http://regdocs.bd.com to access safety data sheets (SDS).
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products




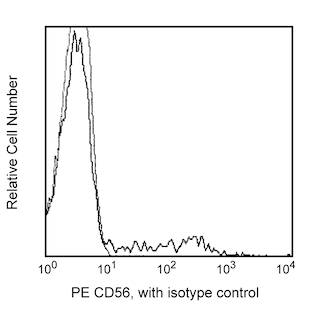
The DX9 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to CD158e1, also known as NKB1. CD158e1 functions as a killer cell inhibitory receptor (KIR) and is encoded by KIR3DL1 (Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor, three domains, long cytoplasmic tail). CD158e1 is a 70 kDa glycoprotein that belongs to the Ig superfamily. It is expressed on a subset of natural killer cells and a small subset of T cells. Expression of CD158e1 has been observed to vary among individuals. KIR molecules specifically recognize a certain group of HLA class I antigens. Interaction of CD158e1 with specific HLA-B antigen on a target cell appears to inhibit cell-mediated cytotoxicity by delivering a negative signal that prevents lymphocyte activation. It is suggested that this MHC class I-KIR interaction works as a signaling mechanism that regulates NK and T-cell responses to antigenic challenge.
Development References (10)
-
D'Andrea A, Chang C, Franz-Bacon K, McClanahan T, Phillips JH, Lanier LL. Molecular cloning of NKB1. A natural killer cell receptor for HLA-B allotypes. J Immunol. 1995; 155(5):2306-2310. (Biology). View Reference
-
D'Andrea A, Chang C, Phillips JH, Lanier LL. Regulation of T cell lymphokine production by killer cell inhibitory receptor recognition of self HLA class I alleles. J Exp Med. 1996; 184(2):789-794. (Biology). View Reference
-
Fry AM, Lanier LL, Weiss A. Phosphotyrosines in the killer cell inhibitory receptor motif of NKB1 are required for negative signaling and for association with protein tyrosine phosphatase 1C. J Exp Med. 1996; 184(1):295-300. (Biology). View Reference
-
Gumperz JE, Paterson JC, Litwin V, et al. Specificity of two anti-class I HLA monoclonal antibodies that block class I recognition by the NKB1 killer cell inhibitory receptor. Tissue Antigens. 1996; 48(4):278-284. (Biology). View Reference
-
Gumperz JE, Valiante NM, Parham P, Lanier LL, Tyan D. Heterogeneous phenotypes of expression of the NKB1 natural killer cell class I receptor among individuals of different human histocompatibility leukocyte antigens types appear genetically regulated, but not linked to major histocompatibililty complex. J Exp Med. 1996; 183(4):1817-1827. (Biology). View Reference
-
Lanier LL, Peterson M, Long EO. Antibody reactivity with NK receptors expressed on transfected cells. In: Mason D. David Mason .. et al., ed. Leucocyte typing VII : white cell differentiation antigens : proceedings of the Seventh International Workshop and Conference held in Harrogate, United Kingdom. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2002:413-414.
-
Litwin V, Gumperz J, Parham P, Phillips JH, Lanier LL. NKB1: a natural killer cell receptor involved in the recognition of polymorphic HLA-B molecules. J Exp Med. 1994; 180(2):537-543. (Biology). View Reference
-
Pascal V, Vivier E, Andre P. CD158 (killer immunoglobulin-like receptors family) report. In: Mason D. David Mason .. et al., ed. Leucocyte typing VII : white cell differentiation antigens : proceedings of the Seventh International Workshop and Conference held in Harrogate, United Kingdom. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2002:412-413.
-
Sivori S, Vitale M, Bottino C, et al. CD94 functions as a natural killer cell inhibitory receptor for different HLA class I alleles: identification of the inhibitory form of CD94 by the use of novel monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1996; 26(10):2487-2492. (Biology). View Reference
-
Wagtmann N, Rajagopalan S, Winter CC, Peruzzi M, Long EO. Killer cell inhibitory receptors specific for HLA-C and HLA-B identified by direct binding and by functional transfer. Immunity. 1995; 3(6):801-809. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.